Engineering helps to make farming environmentally friendly, healthy, and sustainable. Engineers design equipment and develop land planning, planting, and harvesting techniques.
With new and existing equipment, they use automation, accuracy, and smart or "intelligence" technologies. In combination with microcomputers, controllers, artificial intelligence, and other software, sensors are used to optimize the economy's performance, sustainability, and reliability of food, feed, fiber, and fuel.
Agricultural engineering improves ways of reducing crop losses due to field damage during handling, sorting, packaging, and processing.
Food and fiber storage is an important part of the farming industry;
fire, cooling, ventilation, post-harvest handling, logistics, and more are designed by the engineer.
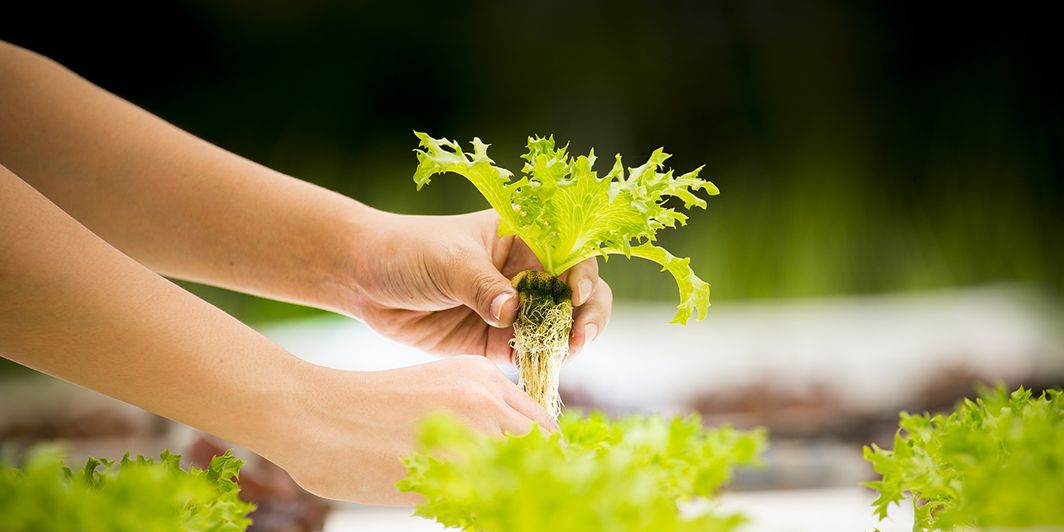
Recent agricultural trends have seen an increase in organic farming, vertical farming, and intensive agriculture to meet the demands of the growing world population and resolve the growing concern for environmental issues.
The major factors that drive the direction and evolution of agricultural research are developments in the field of science and technology along with global urbanization. Food preferences have been altered by increased per capita income in developed countries, occupational shifts, and global linkages. These developments, along with population growth, poses a challenge for agriculture to produce more and better food.
Increased agricultural production by the use of traditional (20th century) farming techniques is a constraint. Because of the dependency on chemical fertilizers and pesticides to improve efficiency and to control pests, the threat to the environment is a major constraint affecting global food output.