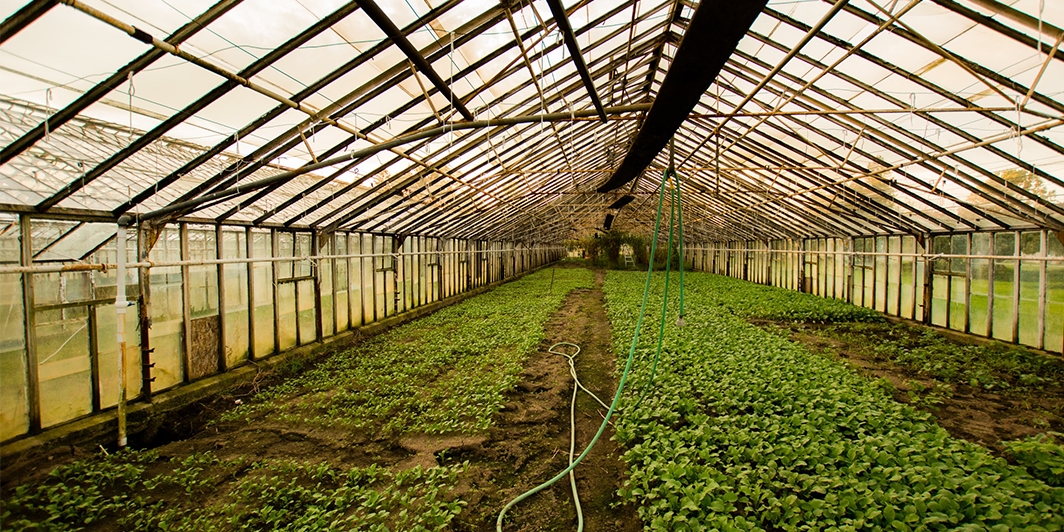
A greenhouse is a structure made mainly of a transparent material such as glass, with walls and roof in which plants that require controlled climatic conditions are grown. From small sheds to industrial-sized houses, these structures vary in scale.
A cold frame is regarded as a miniature greenhouse. A greenhouse aims to protect crops from excess cold or heat and unwanted pests. A greenhouse makes it possible to grow many types of crops year-round, and what a greenhouse most commonly grows are fruits, tobacco plants, vegetables, and flowers.
The location of your greenhouse
In a place that gets plenty of sunshine and would not be susceptible to floods, it is perfect to create your DIY greenhouse. Choosing a site that is flat with stable soil is safest. After your greenhouse is installed, you don't want the soil to change. To drain excess water away from the greenhouse (about 6" drop for each 100 '), we suggest grading the soil with a slight pitch.
You may want to make sure it is an environment that receives plenty of light when determining where to put your greenhouse. South or southeast of any existing structures would be the perfect spot. If that is not an option, to catch most winter sun, the next best position will be east of existing structures. It is safer to avoid building around trees that have too much sunshine blocked out.
What is the perfect Greenhouse Orientation?
Often default to what is better for drainage while avoiding shade from other structures when choosing the orientation of your greenhouse.
Planning to orient your greenhouse east to west to optimize sunlight in the winter months if you are in a northern climate (hardiness zone 6 and lower) and want to expand during the winter months. Otherwise, to get decent light and the best ventilation, orient the greenhouse from North to South.
Before you start building, be sure to develop a greenhouse plan. You want to make sure your plants get maximum sunlight and the structure of your greenhouse is on a solid foundation.